
In this example, it’s the main upstream branch. Then, merge the changes from the upstream branch to the local branch. To sync an upstream repo, first, you need to fetch the upstream changes. Upstream/main Sync Changes From The Upstream repo You can also check out the remote origin and upstream branches using the following command. git/config file and you will see something like below with a remote origin. Add an Upstream Repoīefore adding upstream, you can take a look at your. This way you can pull all the changes happening in the main project repo. You can add the actual repo as an upstream to your local copy. Let’s say you are working on a forked project and you want to sync changes from the main project repo. Tip: With Jenkins multibranch pipelines, you can easily set up the hooks for pull requests from a Forked branch.
When you clone a Forked repository to your local, the forked repository is considered as the remote origin, and the repository you forked from is upstream. So, for your local copy, the actual repository is upstream. Whenever you clone a git repository, you get a local copy in your system.
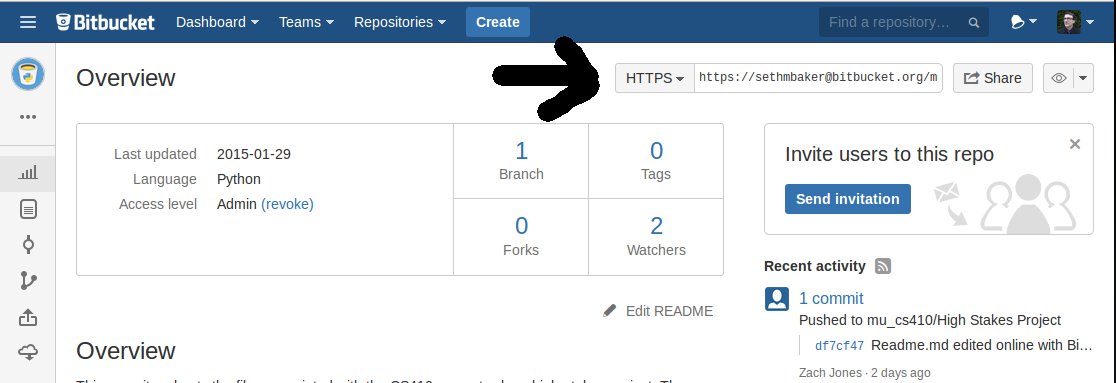
Let’s take a look at different types of git upstreams. For example, when you clone from Github, the remote Github repo is upstream for the cloned local copy. In the git world, upstream refers to the original repo or a branch. Like the literal meaning, upstream refers to something which points to where it originated from. Note: We are following the name “main” instead of “master” considering the removal of terms like “master” and “slave” in the IT community.
#GIT ADD REMOTE ORGIN HOW TO#
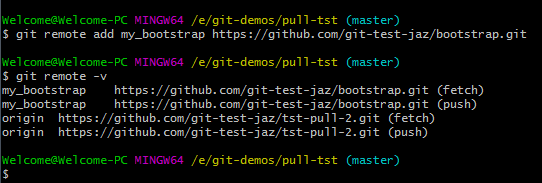
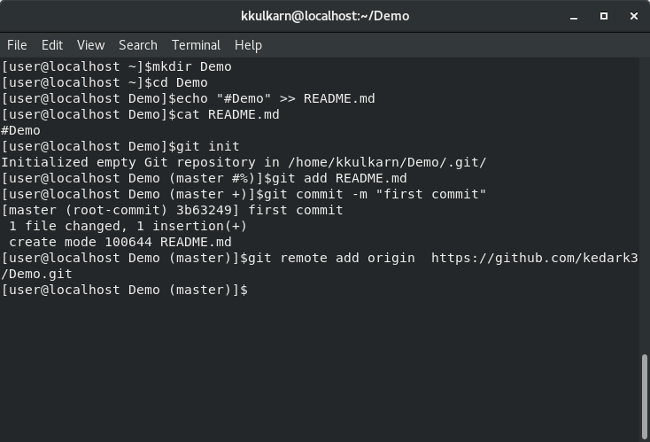
Have you wondered how to keep the forked repo in sync with the main repo? It’s done by adding the main repo as the upstream. You will also learn about different scenarios where git upstream is used and how to apply it in your git development workflow. This can be done by running the git remote command within the local git directory.In this blog, you will learn everything about setting up an upstream for a git repository, a branch and the -set-upstream-to command usage Users need to identify any existing remotes before trying to apply a fix. Since now we have a clear understanding of this error, let’s see how to mitigate it. How to Fix the fatal: remote origin already exists Error The remote add command will attempt to create a new link between the local and the remote repo, and it will create the “fatal: remote origin already exists error” if there is an existing configuration. This is common if the user is trying to follow along with a tutorial without knowing that they have already linked the remote repository or simply forgot that the local repository is already linked to the remote repository (remote “origin” already configured).Īnother reason is trying to change the URL of the “origin” remote repository using the git remote add command. Newcomers to Git will encounter this error if they try to set up an already existing repository. However, the best practice is to adhere to the Git naming convention when naming git branches.Ĭommon Causes for fatal: remote origin already exists Error The name “origin” refers to the default remote, and users can use any name as long as it is compatible with Git.

If there is a remote named “test” in the repository and a user is trying to add a remote with the same name, it will generate the following error Įnter fullscreen mode Exit fullscreen mode The “ origin” in this error refers to the name of the remote. This error occurs when a user tries to link a remote git repository with the local repo using the git remote tool.
#GIT ADD REMOTE ORGIN CODE#
Since Git is a distributed version control system, the data is stored locally until the code is pushed to a remote repository. Users will face this error while attempting to create a remote with the name “origin” when a remote with this name already exists within the git repository. What is fatal: remote origin already exists Error? This article will discuss how to fix the git error: “fatal: remote origin already exists.”
#GIT ADD REMOTE ORGIN SOFTWARE#
Git is the leading version control system powering numerous projects from simple hobby projects to enterprise-grade applications.Īs with any other software system, users may encounter errors while using Git for source code management. A good version control system is critical for the software development life cycle to manage and streamline the development and deployment processes properly.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
